VPN vs Proxy vs Tor What Are The Differences? Best guide

VPN vs Proxy vs Tor What Are The Differences will be described in this article. Virtual private networks, or VPNs, proxies, and Tor are three of the strongest privacy solutions available for enhancing online security. Discover how to compare a proxy vs. VPN and discover the distinctions between Tor, VPNs, and proxy servers by continuing to read. Then, use a renowned VPN to encrypt all of your traffic over a private, fast, and secure connection.
VPN vs Proxy vs Tor What Are The Differences? Best guide
In this article, you can know about VPN vs Proxy vs Tor here are the details below;
Understanding VPNs
With a virtual private web (VPN), you can access the internet from a remote server while your web traffic is encrypted and safe to travel through. Your internet traffic is given a distant IP address when you use a VPN, giving the impression to onlookers that you are physically situated somewhere else in the world.
This Article Contains:
- Recognizing VPNs
- Comprehending proxies
- Comprehending VPN, Tor, and Tor Proxy
- Which service suits me the most?
- Can a VPN and a proxy be used simultaneously?
- Is it possible to utilize Tor along with a proxy?
- Can you use VPN and Tor simultaneously?
- To get the finest ease of use, security, and speed, get a VPN.
A virtual private network (VPN) appears to your computer as simply another network interface. However, if you use a VPN service, like Avast Secureline VPN, you get a unique remote IP address that is only used by your VPN. To appear from a specific location, all you need to do is launch your preferred VPN app.
An outsider who sees your network traffic cannot actually know what you are doing; all they can see is that you are connected to a VPN server via a network. This implies that you can circumvent censorship, get around content limitations, stop hackers and advertising from following you online, and conceal all of your browsing activity, even from your internet assistance provider.
Your web traffic is protected by an encrypted tunnel that is provided by a VPN.Your internet traffic is connected to a safe, encrypted connection thanks to a VPN.
Understanding proxies
An apparatus that interacts with a server on your behalf is called a proxy. You establish a connection with the proxy server first, and it routes your connection to the website’s server. In a similar manner, but in the opposing direction, a so-called reverse proxy manages web traffic for a server.
By connecting to a local router—which establishes the connection to the internet—you can use a local proxy. Not your IP address, but the router’s is what the server sees. With the exception of connecting via the internet, internet proxies are identical. They can change your perceived location, just like VPNs, even though there is no encryption between you and the proxy.
Your internet traffic is routed to the website you are viewing through online proxies. By acting as middlemen, online proxies direct your internet traffic to the websites you visit.
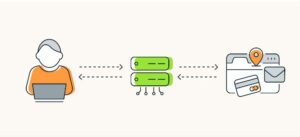
Because a local proxy serves as a middleman, your device isn’t directly accessible to the internet or linked to it. Using an internet proxy might alter your appearance’s location, making it more difficult for someone to identify your data—especially if the proxy is being used frequently.
However, that is just externally visible. On the inside, your internet traffic is still susceptible to monitoring and interception as proxies do not have the encryption that VPNs provide.
Understanding Tor
A software program called Tor (The Onion Router) directs your internet data via a number of networks or relay nodes. Journalists, whistleblowers, and others can access the web anonymously thanks to Tor’s level of anonymity, which is achieved by hiding your internet connection’s origin.
Tor’s layered design is reflected in the name, which makes allusion to onions. When you utilize Tor, your information is transferred to another node after being encrypted and devoid of any personally identifiable information. Your data is decrypted there, and then one of its layers is transferred to another node where the procedure is repeated. It is impossible to determine your actual location or the data’s origin (as defined by the internet) after it reaches its destination.
When using the Tor browser, web traffic is encrypted and decrypted many times.Data that travels via the Tor browser is encrypted multiple times.
Although Tor is a vital tool for anyone looking to avoid being monitored by the government or other authorities, it may equally be used for evil. It is frequently linked to the so-called “darkweb,” a portion of the internet that is only accessible with specialized software (like Tor) and masks the actual location of web traffic. That explains the moniker “dark web.”
Tor is a very powerful tool for protecting your internet data because of its intricate network of nodes and many levels of encryption and decoding. But speed suffers as a result of all that privacy protection. In typical web browsing, even a basic search engine request may take several seconds to process, which might seem like an eternity.
Is Tor a VPN?
While Tor is not a VPN, it does offer some of the features and advantages of one, including robust encryption that conceals your identity, location, and online activities. On the other hand, Tor masks internet traffic by passing it through nodes in the Onion overlay network, as opposed to creating a virtual private network that funnels your data through an encrypted tunnel.
Tor lets you access dark web websites and services like dark web search engines and dark web markets, despite its notoriously poor speed and lack of true end-to-end encryption like a VPN.
Proxy vs VPN vs Tor
There is no way that can ensure total privacy or defense against cyberattacks. However, you must first identify your internet priorities and the amount of work you are willing to put in to achieve them before you can decide which of the three methods—proxy, VPN, or Tor—will help you secure your privacy the best.
For instance, hiding your location with a proxy is easy to do, but it’s not the best option for sending critical data securely. Tor and VPNs provide far greater privacy than proxies, but they also require a little bit more processing power. Furthermore, only a VPN can secure your connection when comparing them to proxies.
Speed
Tor typically has the slowest performance when comparing VPN, proxy, and other service providers since traffic travels via so many different nodes. Additionally, because of the slower connection rates caused by VPN encryption algorithms, proxies are typically faster than VPNs. Thus, you might not require a VPN or Tor if your goal is to speed up your computer or just get over geo-blocking.
A proxy should work just fine for light browsing or to change your IP address. However, proxies are frequently unstable and slow when streaming video, and there is no way to use a proxy to speed up your internet connection.
Your internet traffic is routed across a convoluted network of volunteer networks by Tor, which causes each data packet to travel a significantly longer path from your device to its destination (and vice versa). Although Tor has several privacy benefits, speed isn’t one of them; in fact, it’s usually the slowest of the three.
VPN speeds change based on a number of variables, including server load. However, a few VPN providers have extremely quick upload and download speeds. Additionally, choosing the best VPN server location (such as one that is geographically close) will help you speed up your VPN connection.
Security
Although security proxies are effective at masking your IP address, they cannot encrypt your data or hide your surfing patterns, so you are still vulnerable to other users on the same local network. Therefore, a VPN is required if you wish to connect to public Wi-Fi while maintaining robust security and privacy.
The primary benefit of using Tor over VPNs is that it allows you to access the black web and get beyond government censorship, both of which, depending on your activities and location, can have significant security benefits. Furthermore, substantial levels of anonymity and privacy are provided by the layers of encryption Tor delivers.
VPNs are quicker than Tor and offer greater privacy and stability than proxies. Additionally, the encrypted tunnel that VPN traffic travels through protects your communications and data from being viewed by unscrupulous parties like your ISP or snoopers. With a VPN, the only people who can see your activities are you and your VPN service provider.
Similar to VPNs, Tor networks offer extreme security and anonymity. However, using Tor could result in the NSA being more interested in your surfing habits, and your internet traffic is still potentially susceptible to surveillance at both the input and output nodes.
Esse of use
Proxies are an easy-to-use solution that don’t require installing additional software if you’re looking for a convenient approach to alter your internet location. Proxy servers are useful, but they’re not quite as safe as VPNs or Tor. Any web browser you use has settings that allow you to configure a proxy. Once configured, the proxy is used to process all requests coming from that browser and only that browser.
Setting up Tor isn’t that hard; all you have to do is download and install it. But unless you know where you’re going, it’s difficult to navigate, not very user-friendly, and slow and sluggish to browse on.
Installing software on your device is the initial step towards using a VPN, such as Avast Secureline VPN. Next, before you begin browsing, activate the VPN connection and log in using your user ID and password to set up your VPN. Also check VPN Services
VPNs are the most optimal choice overall. There are a few extra steps involved in utilizing a VPN compared to a proxy, but the privacy benefits are far greater. Although VPNs might not provide the same level of complete anonymity as Tor or provide access to the dark web, they are more user-friendly and have stronger encryption.
It’s not necessary to activate your VPN each time you use a computer. There is no need for a VPN for light browsing. However, you’ll want the added security of a VPN when you operate remotely to complete your company’s expense reports or when handling really sensitive data.
Which service is best for me?
Using a proxy, VPN, or Tor has different advantages based on your online activities and desired level of protection and anonymity. In case you’re a security-conscious casual browser, using a VPN or a proxy server should be sufficient.
If complete privacy isn’t your main concern, proxies are useful for normal browsing and for masking your location so you may access content that might be prohibited in your area. If you need to encrypt your data and are sending critical information, VPNs are a better option. VPNs can also assist you avoid being watched by hiding your IP address.
Tor is especially helpful if you wish to explore the darknet or enhance your browsing experience with additional security and anonymity features. Tor is not necessary for most web users, but it is something you should think about if you wish to hide your traffic.
Determine the significance of the following questions for you:
- Do you want direct communication with another person?
- Do you want other people to be able to read the stuff you give or receive?
- Do you want the websites you visit to be visible to others?
- Are you comfortable having everyone, including the websites you visit, know where you are physically?
Solutions like VPNs, proxies, and anonymizing networks like Tor will increase your digital security and provide you with more peace of mind if any of those claims apply to you.
Can you use a proxy and VPN together?
The answer is no, you cannot use a VPN and a proxy simultaneously. Any proxy settings you may have put up are overridden by a PC VPN client. All of your web traffic is meant to be handled and redirected by a VPN, after all.
Therefore, even though it makes little sense, you could be able to connect to a VPN over an intranet proxy if that is how the local network is set up. When a proxy is used in front of a VPN, the connection is unable to benefit from the additional security features offered by the VPN.
If your VPN is blocked or does not have an endpoint in the region you require, you can also connect to a proxy from your VPN. However, using a VPN in conjunction with a proxy lowers your security because the encryption provided by the VPN ends as soon as your internet traffic leaves it.
Xan you use Tor and a proxy together?
Tor is a network of relays used to deliver encrypted data over the internet. By assigning you your IP server’s address instead of your own, a proxy masks your internet activity. To verify your proxy server, you can pair them using the “Configure” option in your Tor browser, though it’s not apparent how much extra protection that arrangement offers.
If you don’t want the person on the other end of the connection to know that you’re using Tor, or if they are blocking Tor, utilizing Tor to connect to a proxy could be helpful. Although you could connect to Tor using a proxy, doing so isn’t as secure as connecting directly to Tor because your connection to the internet proxy isn’t encrypted. Furthermore, using a proxy with Tor will just slow down your internet connection. Also check VPN Not Working On Android Phones
Having a VPN is helpful if you want to utilize Tor but your local ISP is restricting connections to it.
Can you use Tor and VPN together?
Yes, you can increase your security by utilizing Tor-over-VPN, which combines Tor with a VPN to encrypt your connection with an extra layer of security. The optimal privacy arrangement for you is Tor-over-VPN if privacy is your top priority.
Even while Tor encrypts your data numerous times, the packets are decrypted as they leave Tor and go to their destination, leaving them open to interception.
When you pair a VPN with Tor, you may enjoy end-to-end encryption, meaning that data is encrypted both when it enters and exits the Tor network. Additionally, you can connect to Tor via a VPN without anyone knowing that you’re doing so (and your true IP address will remain concealed).
Install a VPN after downloading Tor if you want to use it in conjunction with one. Next, open the Tor browser and turn on your VPN before beginning your surfing session. Note that your internet connection may become very slow as a result of all this security.
Having a VPN and using Tor together offers strong online security.Layers of encryption and strong security are provided by Tor-over-VPN.
Get a VPN for the best combination of ease, security, and speed
The most practical option for obtaining a private, encrypted, and secure internet connection is, for the most of us, using a VPN. Avast, which has protected over 400 million individuals globally, has the know-how and experience to assist in securing your online presence. Start safely and securely browsing the internet right now by installing Avast SecureLine VPN.