How To Fix The Blue Screen Of Death

How To Fix The Blue Screen Of Death will be discussed in this article. While the “blue screen of death” is unsettling, there is yet hope! A blue net of death (BSOD) can be forced by a wide range of hardware and software problems, most of which are repairable. We’ll walk you through how to resolve the blue screen and save your computer from death. Acquire a specialized tool for optimizing PC performance to ensure optimal system performance.
How To Fix The Blue Screen Of Death
In this article, you can know about How To Fix The Blue Screen Of Death here are the details below;
What does the blue screen of death (BSOD) mean?
The Windows operating system crashes due to a supposed “fatal” system fault, causing the blue screen of death, or BSOD, to appear. The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a warning that Windows has reached a critical state and cannot be operated safely; yet, it is frequently the result of relatively simple issues that are readily resolved.
This Article Contains:
- The blue screen of death (BSOD): what does it mean?
- The blue screen of death is caused by what?
- Typical stop codes for Windows
- How to resolve Windows’ “blue net of death”
- Boost computer speed and avoid crashes.
When a blue net of death (BSOD) occurs on Windows 10 and later, you will see specific messages outlining the issue along with a Windows “stop code” (which can be either text or hexadecimal) that can be looked up on Windows Support for a more thorough explanation of the fault. In Windows 10 or11, a QR code that you can scan to understand more about the crash may also appear on the blue screen.
We’ll examine some of the most typical BSOD causes and provide you with an overview of the most prevalent error codes and their meanings. Alternatively, go ahead and discover how to resolve any problem code to prevent a blue screen of death.
Windows blue screen of deathThe Windows blue screen, which is usually annoying.
What causes the blue screen of death?
Any issue that prevents Windows from operating safely can result in the blue screen of death. Software issues like driver updates that are incompatible or hardware issues like a hard drive that needs to be formatted or overheating from overclocking your CPU can cause the blue screen of death (BSOD).
The Windows error code can be used to specify the precise cause of the blue screen of death (BSOD), which is typically caused by corrupted files or issues with hardware connection. Generally speaking, BSOD causes are not too concerning unless crashes occur frequently. Whatever the reason behind a blue screen of death, frequent tune-ups to keep your computer operating efficiently can typically help prevent it.
Cleaning up your computer by deleting superfluous apps and unwanted files can help speed it up if it has been operating slowly. Avast Cleanup is specialist optimization software that fixes hard disk issues, uninstalls junkware and bloatware, and updates your software automatically.
Common Windows stop codes
The following are a few of the most typical Windows stop codes for issues resulting in the error “blue screen of death”:
· Critical_process_died
If a critical system function has failed, you will see this. It might just be that you terminated important tasks in Task Manager by accident.
· System_thread_exception_not_handle
Often, this is the result of an old or malfunctioning driver. Updating your drivers or going back to an earlier version will help you prevent this from occurring again.
· IRQL_not_less_or_equal
A system process or device software has attempted to access more memory than is permitted. To avoid this problem, check for corrupted system files or update your drivers.
· Video_TDR_timeout_detected
This suggests a processing problem on the GPU. It can be a sign of faulty drivers or the result of you pushing your display adapter to its breaking point.
· Page_fault_in_nonpaged_area
A nonexistent memory address has been referenced by a system process. Either the RAM is broken, or the driver or system process is to blame.
· System_service_exception
The driver or system process that produced this error is frequently listed. When troubleshooting if a system file is marked, proceed with caution. Compared to system patches, driver updates and rollbacks are less dangerous to execute.
· DPC_watchdog_violation
When a device’s driver is outdated or incompatible with the operating system, this occurs. Corrupted system files are also a possibility.
· NTFS_file_system
A portion of the hard drive has become corrupted; this is a common occurrence with aging disks. Damaged segments can be located and fixed by scanning the disk.
· DATA_BUS_ERROR
a general code for hardware problems, indicating that the device is either malfunctioning, incompatible, or configured improperly. If all other options are exhausted, you might have to uninstall the component.
Thankfully, you don’t have to understand how to solve each of these issues separately. For assistance in resolving issues linked to BSOD, go to the information provided below.
How to fix the blue screen of death on Windows
There are numerous ways to remedy a blue screen of death, but fortunately, there is only one procedure you must follow to identify your blue screen of death and address the problem.
Here’s how to resolve a death screen blue screen:
1. Shut down the PC that showed the BSOD
To turn off the computer, press and hold the power button. This is OK as the goal of a proper shutdown is to preserve all temporary data on the machine. If the system has already crashed, it is too late to accomplish that; the only option is to force a shutdown.
2. Disconnect all USB devices except for the mouse and keyboard
Take out any external devices, including printers and hard drives. The error may have been caused by these peripherals and their drivers.
3. Reboot the system in Safe Mode with Networking
Safe Mode is a stripped-down performance of your standard Windows operating system that only permits necessary processes that are extremely unlikely to cause another Blue Screen of Death, providing you more room to fix the issue.
Restarting in Safe Mode involves turning on your computer normally again, holding down the Shift key while choosing Restart from the Power icon when you get the Windows sign-in screen.
Once your computer restarts, the Select an option screen will appear. To restart, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings.
You will be presented with a list of alternatives upon startup. To kick your computer in Safe Mode with Networking, press F5.
4. Uninstall recently instead software
As soon as you’re in Safe Mode, you should uninstall any recently installed software because it’s most likely the source of the problem. Press the Windows key in Windows to uninstall program. On the Add or delete applications page, type “add or remove programs” and click.
Entering “add or remove programs” into the search field opens the Windows start menu.
Next, seek for anything that you may have installed recently or that appears strange by scrolling through the list of programs (but don’t click on anything that has Microsoft in the name). After selecting the application, select Uninstall.
An illustration of “Add or remove programs.” The “Uninstall” button below has been circled in relation to the program that was selected.
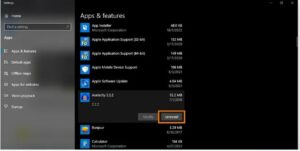
In the process, you want to utilize a junkware removal application to eliminate any unnecessary files and PUPs (potentially unwanted programs) that might be impeding your speed. Once you’ve finished the blue screen of death cure, getting rid of dead weight will assist keep your PC operating properly in addition to clearing up disk space.
5. Roll back or disable drivers
You ought to attempt reversing recent driver upgrades as they might be the problem. Since display adapter drivers and non-essential components are typically the most problematic, it makes the most sense to start there.
First, type “Device manager” into the Windows Keypad and press Enter.
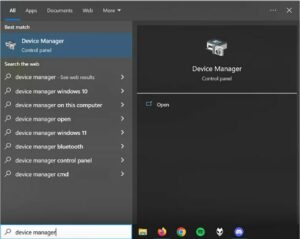
There’s an open Windows start menu. The word “device manager” has been entered.
Next, go through the component list, select an item with a right-click, and select Properties from the menu that appears.
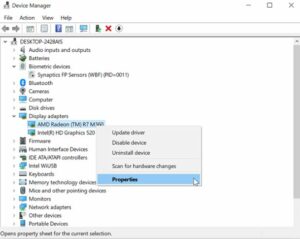
An overview of the device manager. Under “Display adapters,” the AMD display card is selected. Right-clicking on the AMD GPU has the mouse hovering over “Properties.”
Finally, select Roll Back Driver under the Device tab.
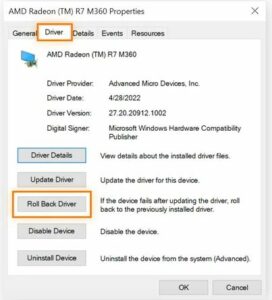
An overview of the display adapter’s properties. The “Roll Back Driver” button is highlighted, and the “Driver” tab has been chosen.
To reverse recent driver upgrades for additional hardware parts, use the same procedure.
6. Scan for malware
The BSOD might have been brought on by malware or a virus that erased or corrupted important system files. Launch your favorite malware removal application, make sure it’s up to date, and perform a comprehensive scan to discover any malware that might be hiding on your device in order to stop additional disturbance and guarantee your PC is secure.
To check for malware on your device, download Avast One.
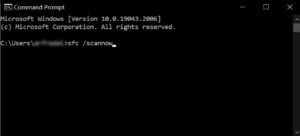
7. Run an SFC Scan
Now is the time to use a System File Checker (SFC) scan to look for corrupted or missing system files and, if feasible, repair or replace them. Here’s how to use Command Prompt to perform a System File Checker scan:
First, type “cmd” using the Windows key. In the Command Prompt, right-click and choose “Run as Administrator.” Choose either “Yes” or “OK” when prompted.
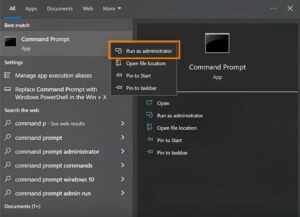
Right-clicking on the command prompt and circling “Run as administrator” has opened the Windows start menu.
Next, open the Command Prompt dialogue box, type sfc /scannow, press Enter, and watch for the scan to finish.
The previously described command has been entered into the command prompt that appears.
8. Scan your hard drive
A CHKDSK hard drive scan looks for physical damage to the disk and corrupted file systems, both of which are major causes of the “blue screen of death.”
Type “cmd” into the Windows keypad to launch a CHKDSK scan. In the Command Prompt, right-click and choose “Run as Administrator.” Click “OK” or “Yes” when requested.
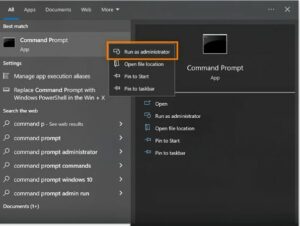
Right-clicking on the command prompt and circling “Run as administrator” has opened the Windows start menu.
Then, to run the command line and start the scan, just type “chkdsk” and press Enter.
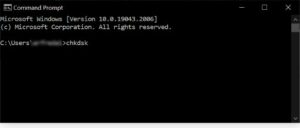
The command prompt appears and “chkdsk” is entered.Should the scan reveal any drive issues, you must launch a fresh CHKDSK procedure in order to fix them. To initiate a more thorough diagnostic scan and repair damaged hard drive sectors so they can be read by the file system, type “chkdsk /r” into Command Prompt and press Enter.
Since hardware ages, you should execute this type of hard drive test on a regular basis if your disk is older than a few years in order to detect problems before they become serious enough to cause a crash.
9. Check your computer’s RAM
Should a BSOD be the result of RAM issues, the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool will assist you in pinpointing the precise problem.
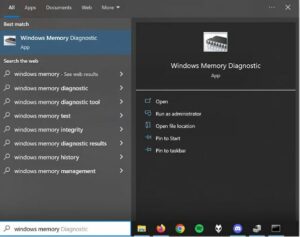
To verify whether the RAM on your computer is operating appropriately, use the Windows key, type “Windows Memory Diagnostic,” and hit Enter.
Windows Memory Diagnostic has been entered after opening the Windows start menu.
When you’re ready, click Restart immediately and (optionally) check for issues.
The option to “Restart now & check for issues” is highlighted when Windows Memory Diagnostic appears.
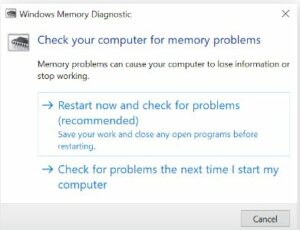
The diagnostic’s findings will become visible as soon as your machine restarts. You can view them in the Event Viewer if you would like to refer to them once more.
10. Restart your PC to see if the BSOD shows again
Now is the ideal moment to reset and determine whether any of the previously suggested changes have worked, as the RAM check requires a reboot. Congratulations if the BSOD has disappeared! You’ve figured out the answer.
If so, you can begin very carefully reinstalling drivers and software that you had previously rolled back or deleted. Just create sure you download them from reliable sources and install each one individually while leaving other programs open. It’s advisable to update the Windows drivers first, then the audio and graphics drivers.
Use a driver updater to assist maintain your drivers updated for best performance. This will not only spare you from having to set up updates by hand, but a specialized tool can also lessen the likelihood of issues occurring throughout the installation process. Furthermore, it can lessen the chance of experiencing another Windows blue screen.
Similarly, to keep you, your files, and your computer safe and secure, you can also assist prevent Windows blue screens by cleaning your computer on a frequent basis and installing antivirus software.
11. If all else fails, reinstall Windows
Reinstalling Windows is the only remaining option if everything has failed thus far. This is the last option because it would erase all of the data on your computer. Fortunately, you still have the option to backup all of your data and create a hard drive image if you can operate Windows normally in Safe Mode. This allows you to restore Windows and start over from scratch.
Prevent crashes and speed up your computer
Maintaining the optimal arrangement of your PC with routine tune-ups that stop minor issues from developing into major issues later on is a wonderful strategy to fend off the blue screen of death.
By automatically eliminating clutter and bloatware, defragging the hard drive, repairing disk issues, and maintaining software updates, Avast Cleanup keeps your computer completely optimized. Experience lag-free, quick performance by downloading and trying Avast Cleanup now.